EKS GPU Cluster from Zero to Hero
Introduction
If you ever tried to run a GPU workload on Kubernetes cluster, you know that this task requires non-trivial configuration and comes with high cost tag (GPU instances are quite expensive).
This post shows how to run a GPU workload on Kubernetes cluster in cost effective way, using AWS EKS cluster, AWS Auto Scaling, Amazon EC2 Spot Instances and some Kubernetes resources and configurations.
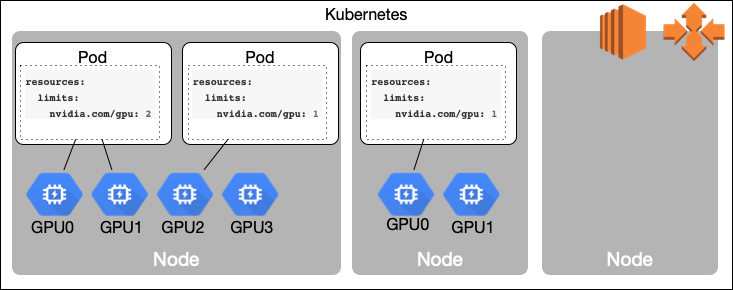
EKS Cluster Plan
First we need to create a Kubernetes cluster that consists from mixed nodes, non-GPU nodes for management and generic Kubernetes workload and more expensive GPU nodes to run GPU intensive tasks, like machine learning, medical analysis, seismic exploration, video transcoding and others.
These node groups should be able to scale on demand (scale out and scale in) for generic nodes, and from 0 to required number and back to 0 for expensive GPU instances. More than that, in order to do it in cost effective way, we are going to use Amazon EC2 Spot Instances both for generic nodes and GPU nodes.
AWS EC2 Spot Instances
With Amazon EC2 Spot Instances instances you can save up to 90% comparing to On-Demand price. Previously, Spot instances were terminated in ascending order of bids. The market prices fluctuated frequently because of this. In the current model, the Spot prices are more predictable, updated less frequently, and are determined by Amazon EC2 spare capacity, not bid prices. AWS EC2 service can reclaim SPot instances when there is not enough capacity for specific instance in specific Availability Zone. Spot instances receive a 2 minute alert when are about to be reclaimed by Amazon EC2 service and can use this time for graceful shutdown and state change.
The Workflow
Create EKS Cluster
It is possible to create AWS EKS cluster, using AWS EKS CLI, CloudFormation or Terraform, AWS CDK or eksctl.
eksctl CLI tool
In this post eksctl (a CLI tool for creating clusters on EKS) is used.
It is possible to pass all parameters to the tool as CLI flags or configuration file. Using configuration file makes process more repeatable and automation friendly.
eksctl can create or update EKS cluster and additional required AWS resources, using CloudFormation stacks.
Customize your cluster by using a config file. Just run
eksctl create cluster -f cluster.yaml
to apply a cluster.yaml file:
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: test-cluster
region: us-west-2
nodeGroups:
- name: ng
instanceType: m5.large
desiredCapacity: 10
A new EKS cluster with 10 m5.large On-Demand EC2 worker nodes will be created and cluster credentials will be added to ~/.kube/config file.
Creating node groups
As planned, we are going to create two node groups for Kubernetes worker nodes:
- General node group - autoscaling group with Spot instances to run Kubernetes system workload and non-GPU workload
- GPU node groups - autoscaling group with GPU-powered Spot Instances, that can scale from 0 to required number of instances and back to 0.
Fortunately, the eksctl supports adding Kubernetes node groups to EKS cluster and these groups can be composed from Spot-only instances or mixture of Spot and On-Demand instances.
General node group
The eksctl configuration file contains EKS cluster in us-west-2 across 3 Availability Zones and the first General autoscaling (from 2 to 20 nodes) node group running on diversified Spot instances.
---
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: gaia-kube
region: us-west-2
availabilityZones: ["us-west-2a", "us-west-2b", "us-west-2c"]
nodeGroups:
# spot workers NG - multi AZ, scale from 3
- name: spot-ng
ami: auto
instanceType: mixed
desiredCapacity: 2
minSize: 2
maxSize: 20
volumeSize: 100
volumeType: gp2
volumeEncrypted: true
iam:
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonEC2RoleforSSM
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly
withAddonPolicies:
autoScaler: true
ebs: true
albIngress: true
cloudWatch: true
instancesDistribution:
onDemandPercentageAboveBaseCapacity: 0
instanceTypes:
- m4.2xlarge
- m4.4xlarge
- m5.2xlarge
- m5.4xlarge
- m5a.2xlarge
- m5a.4xlarge
- c4.2xlarge
- c4.4xlarge
- c5.2xlarge
- c5.4xlarge
spotInstancePools: 15
tags:
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled: 'true'
labels:
lifecycle: Ec2Spot
privateNetworking: true
availabilityZones: ["us-west-2a", "us-west-2b", "us-west-2c"]
### next: GPU node groups ...
Now it is time to explain some parameters used in the above configuration file.
ami: auto-eksctlautomatically discover latest EKS-Optimized AMI image for worker nodes, based on specified AWS region, EKS version and instance type. See Amazon EKS-Optimized AMI chapter in User GuideinstanceType: mixed- specify that actual instance type will be one of instance types defined ininstancesDistributionsectioniamcontains list of predefined and in-place IAM policies;eksctlcreates a new IAM Role with specified policies and attaches this role to every EKS worker node. There are several IAM policies you are required to attach to every EKS worker node, read Amazon EKS Worker Node IAM Role section in User Guide andeksctlIAM policies documentationinstancesDistribution- specify mixed instance policy for EC2 Auto Scaling Groups, read AWS MixedInstancesPolicy documentationspotInstancePools- specifies number of Spot instance pools to use, read moretags- AWS tags added to EKS worker nodesk8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabledwill use this tag for Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler auto-discovery
privateNetworking: true- all EKS worker nodes will be placed into private subnets
Spot Instance Pools
When you are using Spot instances as worker nodes you need to diversify usage to as many Spot Instance pools as possible. A Spot Instance pool is a set of unused EC2 instances with the same instance type (for example, m5.large), operating system, Availability Zone, and network platforms.
The eksctl currently supports single Spot provisioning model: lowestPrice allocation strategy. This strategy allows creation of a fleet of Spot Instances that is both cheap and diversified. Spot Fleet automatically deploys the cheapest combination of instance types and Availability Zones based on the current Spot price across the number of Spot pools that you specify. This combination allows avoiding the most expensive Spot Instances.
The Spot instance diversification also increases worker nodes availability, typically not all Spot Instance pools will be interrupted at the same time, so only a small portion of your workload will be interrupted and EC2 Auto-scaling group will replace interrupted instances from others Spot Instance pools.
GPU-powered node group
The next part of our eksctl configuration file contains first GPU autoscaling (from 0 to 10 nodes) node group running on diversified GPU-powered Spot instances.
When using GPU-powered Spot instances, it’s recommended to create GPU node group per Availability Zone and configure Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler to avoid automatic ASG rebalancing.
Why is it important?
GPU-powered EC2 Spot Instances have relatively high Frequency of interruption rate (>20% for some GPU instance types) and using multiple AZ and disabling automatic Cluster Autoscaler balancing can help to minimize GPU workload interruptions.
# ... EKS cluster and General node group ...
# spot GPU NG - west-2a AZ, scale from 0
- name: gpu-spot-ng-a
ami: auto
instanceType: mixed
desiredCapacity: 0
minSize: 0
maxSize: 10
volumeSize: 100
volumeType: gp2
volumeEncrypted: true
iam:
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonEC2RoleforSSM
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly
withAddonPolicies:
autoScaler: true
ebs: true
fsx: true
efs: true
albIngress: true
cloudWatch: true
instancesDistribution:
onDemandPercentageAboveBaseCapacity: 0
instanceTypes:
- p3.2xlarge
- p3.8xlarge
- p3.16xlarge
- p2.xlarge
- p2.8xlarge
- p2.16xlarge
spotInstancePools: 5
tags:
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/taint/dedicated: nvidia.com/gpu=true
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/label/nvidia.com/gpu: 'true'
k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/enabled: 'true'
labels:
lifecycle: Ec2Spot
nvidia.com/gpu: 'true'
k8s.amazonaws.com/accelerator: nvidia-tesla
taints:
nvidia.com/gpu: "true:NoSchedule"
privateNetworking: true
availabilityZones: ["us-west-2a"]
# create additional node groups for other `us-west-2b` and `us-west-2c` availability zones ...
Now, it is time to explain some parameters used to configure GPU-powered node group.
ami: auto-eksctlautomatically discover latest EKS-Optimized AMI image with GPU support for worker nodes, based on specified AWS region, EKS version and instance type. See Amazon EKS-Optimized AMI with GPU support User Guideiam: withAddonPolicies- if a planned workload requires access to AWS storage services, it is important to include additional IAM policies (auto-generated byeksctl)efs: true- enable access to Amazon EFSfsx: true- enable access to Amazon FSx for Lustre
tags- AWS tags added to EKS worker nodesk8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/taint/dedicated: nvidia.com/gpu=true- Kubernetes node taintk8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/label/nvidia.com/gpu: 'true'- Kubernetes node label used by Cluster Autoscaler to scale ASG from/to 0
taintsnvidia.com/gpu: "true:NoSchedule"- Kubernetes GPU node taint; helps to avoid placement on non-GPU workload on expensive GPU nodes
EKS Optimized AMI image with GPU support
In addition to the standard Amazon EKS-optimized AMI configuration, the GPU AMI includes the following:
- NVIDIA drivers
- The
nvidia-docker2package - The
nvidia-container-runtime(as the default runtime)
Scaling a node group to/from 0
From Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler 0.6.1 - it is possible to scale a node group to/from 0, assuming that all scale-up and scale-down conditions are met.
If you are using nodeSelector you need to tag the ASG with a node-template key k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/label/ and k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler/node-template/taint/ if you are using taints.
Scheduling GPU workload
Schedule based on GPU resources
The NVIDIA device plugin for Kubernetes exposes the number of GPUs on each nodes of your cluster. Once the plugin is installed, it’s possible to use nvidia/gpu Kubernetes resource on GPU nodes and for Kubernetes workloads.
Run this command to apply the Nvidia Kubernetes device plugin as a daemonset running only on AWS GPU-powered worker nodes, using tolerations and nodeAffinity
kubectl create -f kubernetes/nvidia-device-plugin.yaml
kubectl get daemonset -nkube-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
aws-node 5 5 5 5 5 <none> 8d
kube-proxy 5 5 5 5 5 <none> 8d
nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset-1.12 3 3 3 3 3 <none> 8d
ssm-agent 5 5 5 5 5 <none> 8d
using nvidia-device-plugin.yaml Kubernetes resource file
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: nvidia-device-plugin-daemonset-1.12
namespace: kube-system
spec:
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nvidia-device-plugin-ds
spec:
tolerations:
- key: nvidia.com/gpu
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- image: nvidia/k8s-device-plugin:1.11
name: nvidia-device-plugin-ctr
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop: ["ALL"]
volumeMounts:
- name: device-plugin
mountPath: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
volumes:
- name: device-plugin
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- p3.2xlarge
- p3.8xlarge
- p3.16xlarge
- p3dn.24xlarge
- p2.xlarge
- p2.8xlarge
- p2.16xlarge
Taints and Tolerations
Kubernetes taints allow a node to repel a set of pods. Taints and tolerations work together to ensure that pods are not scheduled onto inappropriate nodes. One or more taints are applied to a node; this marks that the node should not accept any pods that do not tolerate the taints. Tolerations are applied to pods, and allow (but do not require) the pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
See Kubernetes Taints and Tolerations documentation for more details.
In order to run GPU workload to run on GPU-powered Spot instance nodes, with nvidia.com/gpu: "true:NoSchedule" taint, the workload must include both matching tolerations and nodeSelector.
Kubernetes deployment with 10 pod replicas with nvidia/gpu: 1 limit:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cuda-vector-add
labels:
app: cuda-vector-add
spec:
replicas: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cuda-vector-add
template:
metadata:
name: cuda-vector-add
labels:
app: cuda-vector-add
spec:
nodeSelector:
nvidia.com/gpu: "true"
tolerations:
- key: "nvidia.com/gpu"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
containers:
- name: cuda-vector-add
# https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.7.11/test/images/nvidia-cuda/Dockerfile
image: "k8s.gcr.io/cuda-vector-add:v0.1"
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1 # requesting 1 GPU
Deploy cuda-vector-add deployment and see how new GPU-powered nodes are added to the EKS cluster.
# list Kubernetes nodes before running GPU workload
NAME ID TYPE
ip-192-168-151-104.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2b/i-01d4c83eaee18b7b3 c4.4xlarge
ip-192-168-171-140.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2c/i-07ec09fd128e1393f c4.4xlarge
# deploy GPU workload on EKS cluster with tolerations for nvidia/gpu=true
kubectl create -f kubernetes/examples/vector/vector-add-dpl.yaml
# list Kubernetes nodes after several minutes to see new GPU nodes added to the cluster
kubectl get nodes --output="custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,ID:.spec.providerID,TYPE:.metadata.labels.beta\.kubernetes\.io\/instance-type"
NAME ID TYPE
ip-192-168-101-60.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2a/i-037d1994fe96eeffc p2.16xlarge
ip-192-168-139-227.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2b/i-0038eb8d2c795fb40 p2.16xlarge
ip-192-168-151-104.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2b/i-01d4c83eaee18b7b3 c4.4xlarge
ip-192-168-171-140.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2c/i-07ec09fd128e1393f c4.4xlarge
ip-192-168-179-248.us-west-2.compute.internal aws:///us-west-2c/i-0bc0853ef26c0c054 p2.16xlarge
As you can see, 3 new GPU-powered nodes (p2.16xlarge), across 3 AZ, had been added to the cluster. When you delete GPU workload, the cluster will scale down GPU node group to 0 after 10 minutes.
Summary
Follow this tutorial to create an EKS (Kubernetes) cluster with GPU-powered node group, running on Spot instances and scalable from/to 0 nodes.
References
- EKS Spot Cluster GitHub repository with code for this blog
- The definitive guide to running EC2 Spot Instances as Kubernetes worker nodes by Ran Sheinberg
- Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler
- Taints and Tolleratoins Kubernetes documentation
Disclaimer
It does not matter where I work, all my opinions are my own.